Fragment-based screening is now well-established as a powerful approach to early drug ("lead") discovery.
Email: [email protected]
Tel: +44 (0) 1235 778926
XChemExplorer (XCE) is the counterpart to SoakDB on the data analysis side. It manages large-scale processing and analysis of the x-ray diffraction data, provides an interface to PanDDA, and guides the validation workflow for PanDDA-derived models. It is enormously powerful, and an eye-opener if you've been trying to get through your structures using ccp4 or phenix interfaces.
You can read the XCE brief manual and check for ongoing upgrades and submit issues and suggestions to github.
XCE can be downloaded and adjusted from github, but with no software support; be sure to subscribe to XCHEMBB. If you have the latest CCP4 installed, this will at least launch on your machine, though making it actually work on non-Diamond systems might be a different matter: possible, and we'd be happy to help, but out of our own scope.
PanDDA was developed by Nicholas Pearce to find and extract weak density from large numbers of datasets. The software is distributed with CCP4, and detailed instructions can be found here.
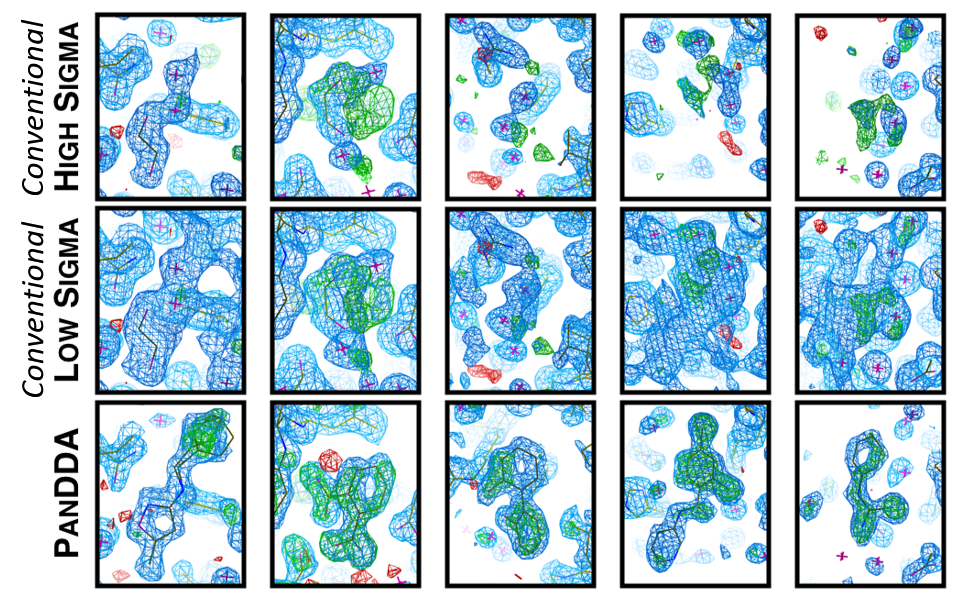
Pearce, N., Krojer, T., Bradley, A. et al. A multi-crystal method for extracting obscured crystallographic states from conventionally uninterpretable electron density. Nat Commun 8, 15123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15123
We have been building a Cloud-based platform where your XChem hits can both be publicised, but also analysed for progressing to potency. Thus, all the screens performed by the SGC, which are made fully public immediately, are served on Fraglaysis, and help demonstrate a new paradigm of serving structural ligand-binding data. Users are free to volunteer their data too.
Fragalysis also enables picking and calculating compounds with approximately cutting-edge computational tools, which we try to make as simple to access as possible to use. Thanks to a big investment from Janssen via the IMI-funded ULTRA-DD project, Fragalysis is now quickly turning from prototype into useful thing.
Fragalysis itself: fragalysis.diamond.ac.uk
Background, descriptions and development priorities at the fragalysis wiki
Diamond Light Source is the UK's national synchrotron science facility, located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire.
Copyright © 2022 Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source Ltd
Diamond House
Harwell Science & Innovation Campus
Didcot
Oxfordshire
OX11 0DE
Diamond Light Source® and the Diamond logo are registered trademarks of Diamond Light Source Ltd
Registered in England and Wales at Diamond House, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot, Oxfordshire, OX11 0DE, United Kingdom. Company number: 4375679. VAT number: 287 461 957. Economic Operators Registration and Identification (EORI) number: GB287461957003.