The principle of the Energy Dispersive EXAFS (EDE) is based on the diffraction of non monochromatic X-rays by a bent crystal (polychromator crystal). The polychromatic beam is focused on the sample and then diverges towards a position sensitive detector where beam position is correlated to energy. The dispersive configuration of XAS has two main advantages that make it scientifically attractive. First, the whole x-ray absorption spectrum is collected simultaneously which makes the technique especially useful for the study of fast processes. Second, the size of the focussed beam at the sample position is small and very stable due to the fact that no movement of optical elements is required to collect the spectral data.
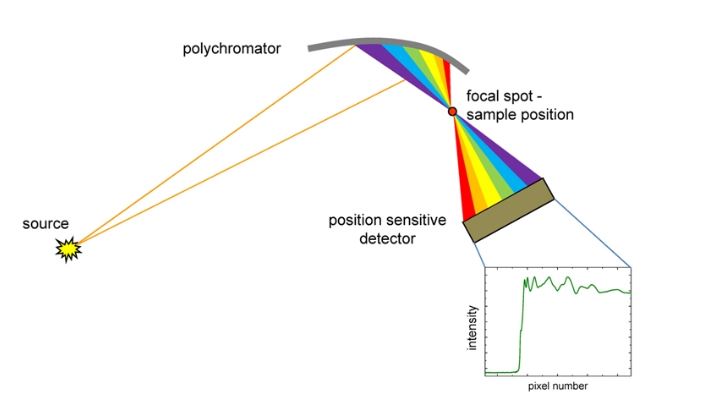
Some examples of science where this technique plays an important role are listed below.
[1] (a) M.A. Newton, A.J. Dent, S. Diaz-Moreno, S.G. Fiddy, J. Evans. Angewandte Chemie, International Edition in English, 41, 2587 (2002) (b) M. Tada and Y. Iwasawa, Annual Rewview of Materials Research, 35, 397 (2005).
Diamond Light Source is the UK's national synchrotron science facility, located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire.
Copyright © 2022 Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source Ltd
Diamond House
Harwell Science & Innovation Campus
Didcot
Oxfordshire
OX11 0DE
Diamond Light Source® and the Diamond logo are registered trademarks of Diamond Light Source Ltd
Registered in England and Wales at Diamond House, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot, Oxfordshire, OX11 0DE, United Kingdom. Company number: 4375679. VAT number: 287 461 957. Economic Operators Registration and Identification (EORI) number: GB287461957003.