Keep up to date with the latest research and developments from Diamond. Sign up for news on our scientific output, facility updates and plans for the future.
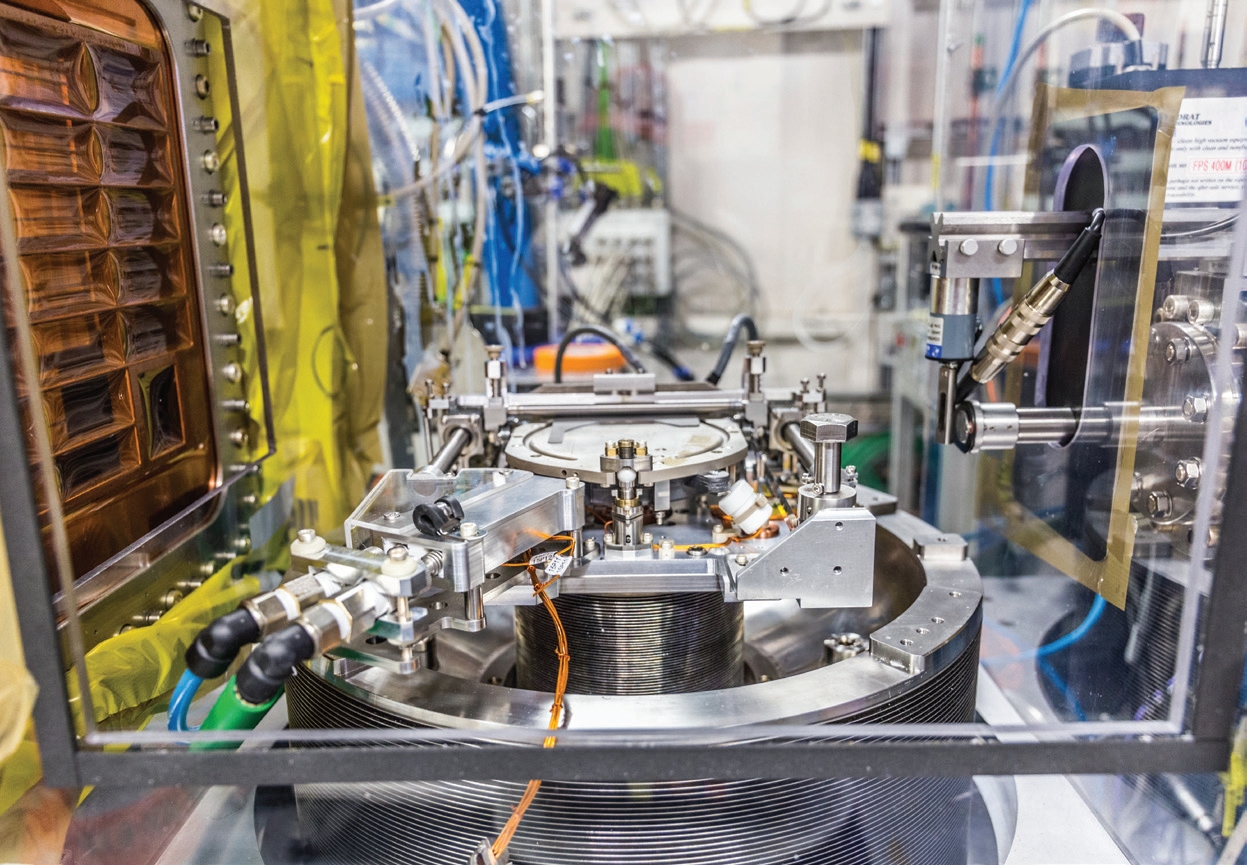
The Soft Condensed Matter (SCM) Village at Diamond Light Source provides scientific capabilities for the investigation of biological samples and inorganic systems using infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV) and X-ray radiation. The SCM village consists of four beamlines divided into the two X-ray scattering beamlines (B21 and I22) and spectroscopy beamlines (B22 and B23). Together, these beamlines can provide experimental investigations on samples in the solution state, fixed inside living cells or deposited as thin-films.
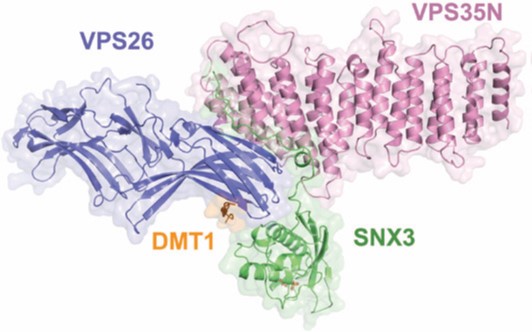 Recycling has become commonplace in our everyday life, and is evident in reduction in the consumption of resources, saving energy and minimising waste. Similarly, cells constantly recycle proteins and lipids, with a direct impact on nutrient uptake, re-sensitisation to environmental signals, immune surveillance and waste management. Retromer is a multiprotein complex that recycles cargo proteins from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network and the plasma membrane.
Recycling has become commonplace in our everyday life, and is evident in reduction in the consumption of resources, saving energy and minimising waste. Similarly, cells constantly recycle proteins and lipids, with a direct impact on nutrient uptake, re-sensitisation to environmental signals, immune surveillance and waste management. Retromer is a multiprotein complex that recycles cargo proteins from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network and the plasma membrane.
Read more about this B21/I02/I03 highlights.
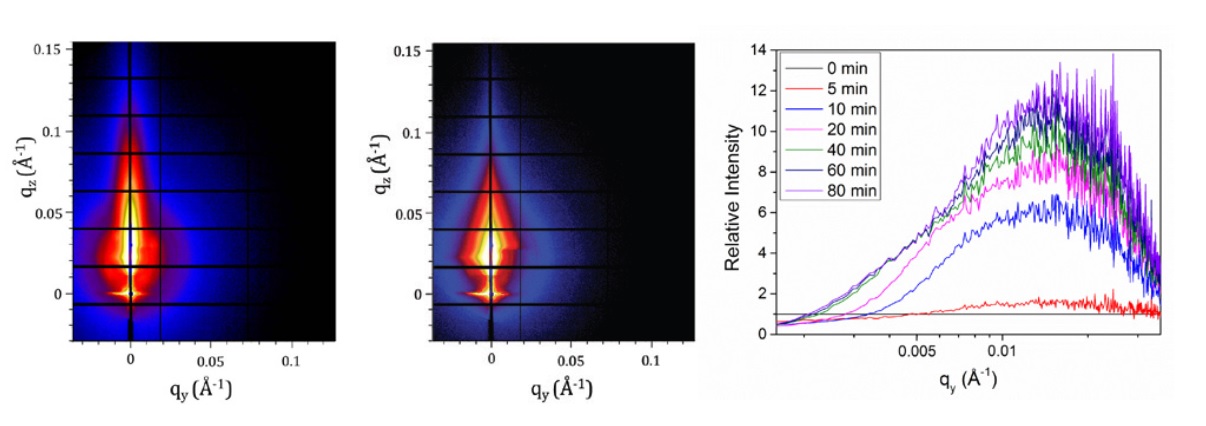 Perovskites are crystalline semiconductors that show great promise as solar cell materials. Perovskite-based solar cells have a similar efficiency of converting sunlight into electricity as conventional silicon-based solar cells, but are potentially cheaper and easier to manufacture. Perhaps the simplest method for producing crystalline perovskites involves heating a thin film of a precursor material for about an hour, thereby promoting crystal growth. To produce a perovskite-based solar cell with the highest efficiency, this process needs to produce a smooth film of large, regular crystals, but current processing techniques often produce rough films composed of many small crystallites and possessing small voids.
Perovskites are crystalline semiconductors that show great promise as solar cell materials. Perovskite-based solar cells have a similar efficiency of converting sunlight into electricity as conventional silicon-based solar cells, but are potentially cheaper and easier to manufacture. Perhaps the simplest method for producing crystalline perovskites involves heating a thin film of a precursor material for about an hour, thereby promoting crystal growth. To produce a perovskite-based solar cell with the highest efficiency, this process needs to produce a smooth film of large, regular crystals, but current processing techniques often produce rough films composed of many small crystallites and possessing small voids.
Read more about this I22 highlights.
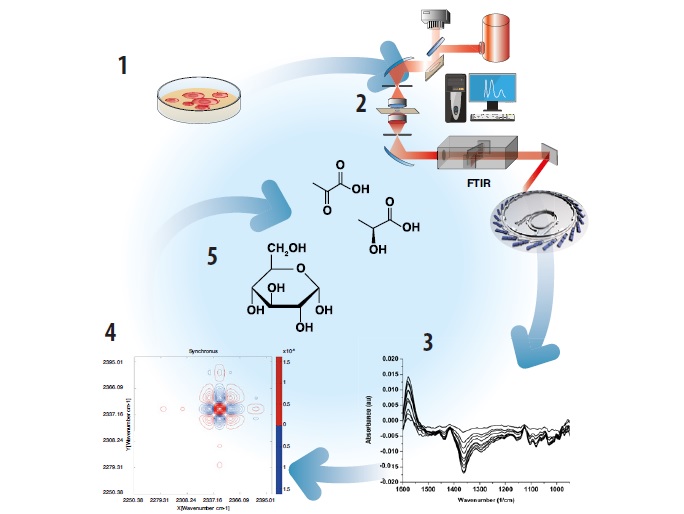 Infrared (IR) spectromicroscopy has been used for the past twenty years to study biological matter because of its sensitivity for detecting sub-cellular components in intact cells and tissues. As the method has improved, attention has turned to the application of this tool for the analysis of biochemical reactions within living cells.
Infrared (IR) spectromicroscopy has been used for the past twenty years to study biological matter because of its sensitivity for detecting sub-cellular components in intact cells and tissues. As the method has improved, attention has turned to the application of this tool for the analysis of biochemical reactions within living cells.
Read more about this B22 highlights.
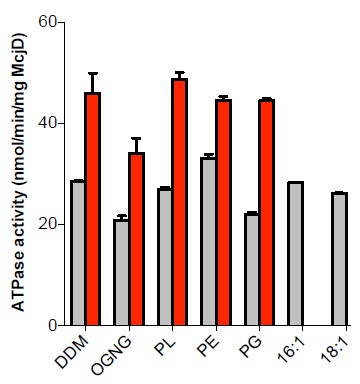 The membrane of a cell is a double-layered structure that is composed of different types of lipids, which can help to support a variety of membrane proteins embedded within them. One such protein, the antibacterial peptide ABC transporter, McjD, is heavily dependent on its neighbouring lipids. McjD transports toxic peptides out of bacterial cells to help protect them, but the specific lipids that assist this activity have not yet been identified.
The membrane of a cell is a double-layered structure that is composed of different types of lipids, which can help to support a variety of membrane proteins embedded within them. One such protein, the antibacterial peptide ABC transporter, McjD, is heavily dependent on its neighbouring lipids. McjD transports toxic peptides out of bacterial cells to help protect them, but the specific lipids that assist this activity have not yet been identified.
Read more about this B23 highlights.
Diamond Light Source is the UK's national synchrotron science facility, located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire.
Copyright © 2022 Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source Ltd
Diamond House
Harwell Science & Innovation Campus
Didcot
Oxfordshire
OX11 0DE
Diamond Light Source® and the Diamond logo are registered trademarks of Diamond Light Source Ltd
Registered in England and Wales at Diamond House, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot, Oxfordshire, OX11 0DE, United Kingdom. Company number: 4375679. VAT number: 287 461 957. Economic Operators Registration and Identification (EORI) number: GB287461957003.