Membrane proteins are essential for many biological processes in organisms ranging from bacteria to humans. In the bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli), a protein called YaeT selects and folds other proteins before inserting them into the outer membrane of the cell. Tim Knowles and his colleagues at the University of Birmingham have been using Diamond Light Source to study protein solution structures in order to understand the processes by which they are targeted in the cell, and how they are folded at their destinations. This is the first time that the full structure of YaeT’s soluble domain has been visualized due to difficulties in creating crystals.
In Detail
Membranes of Gram-negative bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts receive and fold b -barrel trans-membrane proteins through the action of polypeptide transport-associated (POTRA) domains of YaeT and its relatives. In E. coli, folding substrates are inserted into the outer membrane by the protein YaeT, which is essential for viability as its depletion leads to severe Outer Membrane Protein (OMP) biogenic defects.
"These structures help us to understand how proteins are folded into outer membranes - it's important fundamental biology and may also reveal new mechanisms that can be targeted for the design of new antimicrobial agents."Michael Overduin, University of Birmingham
This study combined Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to reveal the structure of all five POTRA domains of YaeT. Previous studies have indicated that all five POTRA domains conserved in YaeT proteins play crucial and interrelated roles in the assembly and functioning of the b -barrel folding apparatus. The elucidation of this solution structure shows that the POTRA domains form an elongated structure that differs from the crystallized state reported earlier in Science by Daniel Kahne and colleagues.
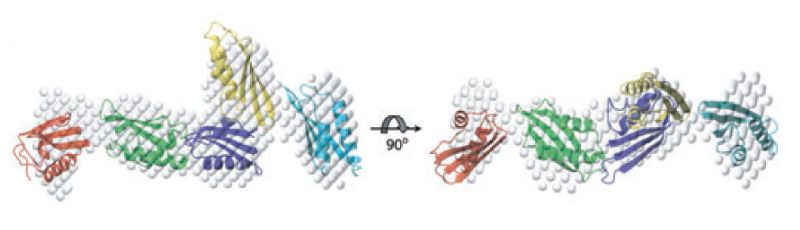
Small-angle X-ray scattering of YaeT’s soluble domain. A. Solvated molecular envelope of the five POTRA domains calculated from the SAXS data
Timothy J. Knowles, Mark Jeeves, Saeeda Bobat, Felician Dance, Darren McClelland, Tracy Palmer, Michael Overduin, Ian R. Henderson, Fold and function of polypeptide transport-associated domains responsible for delivering unfolded proteins to membranes, Molecular Microbiology 68 (5) , 1216–1227
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06225.x
Diamond Light Source is the UK's national synchrotron science facility, located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire.
Copyright © 2022 Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source Ltd
Diamond House
Harwell Science & Innovation Campus
Didcot
Oxfordshire
OX11 0DE
Diamond Light Source® and the Diamond logo are registered trademarks of Diamond Light Source Ltd
Registered in England and Wales at Diamond House, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot, Oxfordshire, OX11 0DE, United Kingdom. Company number: 4375679. VAT number: 287 461 957. Economic Operators Registration and Identification (EORI) number: GB287461957003.