____________________________________
Industrial Liaison Group:
Tel: +44 (0) 1235 778797
E-mail: [email protected]
 Discovering a potent and highly selective API is only part of the story of creating a new medicine. Careful consideration of the appropriate dosage form for the patient is essential for effective treatment.
Discovering a potent and highly selective API is only part of the story of creating a new medicine. Careful consideration of the appropriate dosage form for the patient is essential for effective treatment.
Diamond provides a range of techniques that support the challenges of pharmaceutical formulations, including investigating the dissolution process, particle size, drug and excipient phase behaviour, along with the effects of polymorphism, solubility and oxidation among others.
Below are some examples of how these techniques have been applied.
Many patients suffering from chronic conditions such as diabetes, schizophrenia and acromegaly are required to administer treatments subcutaneously or intramuscularly using injections.
Whilst the efficacy of these treatments has been well documented, the absorption mechanisms, the impact of different formulations and their delivery, is not yet fully understood.
The ability to modulate drug delivery at therapeutically effective doses over a sustained period of time, in vivo, is very challenging. In the case of poorly water-soluble drugs this requires a carefully designed matrix to manage and maintain their controlled release.
Lipid cubic phase carriers offer an effective way to transport both small molecules and larger proteins through oral and parenteral routes (those outside of the digestive tract), as well as local delivery via subcutaneous and intramuscular routes. Complex interactions between the drug and the lipid matrix govern the release profile; for hydrophilic drugs, release can be very fast. The carriers can also be compromised by naturally occurring lipolytic enzymes which act to break down the lipid microstructure.
Read more...
Drug products in the pharmaceutical industry are commonly prepared in the form of discrete multi-particulate units. Bead products are a vehicle used in the development of controlled release drugs and are prepared by coating an inert spherical core with multiple layers, including that of the active ingredient. Components in each applied layer can have a significant impact on how the drug will be released and porosity of the layers is a critical feature related to observed dissolution behaviour. However accurate and highly resolved measurement of the physical integrity of these layers is a significant challenge in the development of advanced multi-particulate dosage forms.
Read more...Medicinal products extracted from biological sources, called biopharmaceuticals or biologics, must be carefully produced to ensure that only high purity active material is generated. Biopharmaceutical manufacturing processes can have an impact on the amount of product-related variants in the final clinical material. Understanding and controlling amounts of these product-related variants is a major challenge in the development of biopharmaceutical products.
Read more...
Drug products are manufactured to an extremely high standard to maintain product safety when taken by patients. Specifications used throughout the manufacturing process cover not only the drug itself, but also the level of potential impurities (chemical, solvent, or polymorph), which are set to limits that are monitored by regulatory bodies to uphold safety and product quality requirements. X-ray powder diffraction is a key analytical technique in the pharmaceutical industry for characterising drug compounds. This is used for throughout the development process to fingerprint compounds and quantify impurities.
Read more...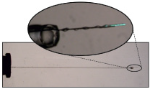
Along with many pharmaceutical materials, sodium diclofenac, a commonly used painkiller, can crystallise in many different forms depending on the manufacturing and formulation conditions. Each crystalline form may have very different biological and physical properties including bioavailability, drug delivery mechanism and shelf-life. Full characterisation and optimisation of solid forms of an API is therefore critical.
Read more...Diamond Light Source is the UK's national synchrotron science facility, located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire.
Copyright © 2022 Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source Ltd
Diamond House
Harwell Science & Innovation Campus
Didcot
Oxfordshire
OX11 0DE
Diamond Light Source® and the Diamond logo are registered trademarks of Diamond Light Source Ltd
Registered in England and Wales at Diamond House, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot, Oxfordshire, OX11 0DE, United Kingdom. Company number: 4375679. VAT number: 287 461 957. Economic Operators Registration and Identification (EORI) number: GB287461957003.