____________________________________
Industrial Liaison Group:
Tel: +44 (0) 1235 778797
E-mail: [email protected]
Drug products in the pharmaceutical industry are commonly prepared in the form of discrete multi-particulate units. Bead products are a vehicle used in the development of controlled release drugs and are prepared by coating an inert spherical core with multiple layers, including that of the active ingredient. Components in each applied layer can have a significant impact on how the drug will be released and porosity of the layers is a critical feature related to observed dissolution behaviour. However accurate and highly resolved measurement of the physical integrity of these layers is a significant challenge in the development of advanced multi-particulate dosage forms.
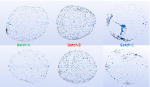
One Pfizer late stage candidate is layered onto an inert sugar core along with several other layers to create the final dosage form. Notable differences in dissolution rates between batches of beads had been observed at Pfizer and it was vital to both understand the reason for this and ensure consistent manufacture in the future. Previous surface and cross-sectional measurements using conventional SEM and benchtop X-ray microtomography had been attempted, but neither provided sufficient resolution. In this case the outer cellulose acetate layer is only ~ 7 μm thick and the pores within that layer are much smaller.
High resolution X-ray tomography measurements were performed on the Diamond Manchester Imaging beamline I13-2 at the Diamond Light Source. Beads from 3 different production batches with varying dissolution profiles were mounted in glass capillaries for imaging. Tomographic analysis was successfully able to distinguish porosity differences between the different production batches and there was correlation between the porosity and the dissolution rate of the beads.
The non-destructive measurement of drug multi-particulates on I13-2 has enabled highly resolved data to be obtained. This has been used to successfully differentiate between different production batches and has highlighted the importance of the integrity of the bead coating in determining the dissolution rate.
For further information, please read our article.

.png)
Diamond Light Source is the UK's national synchrotron science facility, located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire.
Copyright © 2022 Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source Ltd
Diamond House
Harwell Science & Innovation Campus
Didcot
Oxfordshire
OX11 0DE
Diamond Light Source® and the Diamond logo are registered trademarks of Diamond Light Source Ltd
Registered in England and Wales at Diamond House, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot, Oxfordshire, OX11 0DE, United Kingdom. Company number: 4375679. VAT number: 287 461 957. Economic Operators Registration and Identification (EORI) number: GB287461957003.