____________________________________
Industrial Liaison Group:
Tel: +44 (0) 1235 778797
E-mail: industry@diamond.ac.uk
X-ray structural investigation of macromolecules (proteins, viruses, enzymes etc) is a complex and time consuming process where the quality of information obtained about the three-dimensional structure is strongly dependent on the quality of crystals produced. Therefore, the structures of many important targets of pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry remain unknown simply because researchers are unable to obtain crystals of sufficiently high quality or size.
On Earth, the process of macromolecular crystallization is affected by gravity; a force which causes sedimentation and convection due to a variety of sizes and molecular weights of molecules in the crystallization solution. This often results in a yield of crystals that are too small or disordered to be studied by X-ray diffraction.
Researchers from Confocal Science Inc., used Diamond’s macromolecular crystallography data collection service to study samples that were literally out of this world. In the unique space environment, the limitations of gravity no longer apply and high quality crystals can be produced. Confocal Science Inc., an integrated service company for protein crystallography based in Japan, is working in collaboration with several Japanese research partners including the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to grow protein crystals in space on the International Space Station.
Alpha-amylase crystals grown in space (top) (Image courtesy JAXA) were compared to those grown on Earth and the resulting electron density maps are shown. Crystals grown in space tend to grow with higher quality and are sometimes larger compared with crystals growth on Earth. One benefit of this is that ultra-high resolution protein structures can be obtained by X-ray crystallography. Some of the proteins grown include: lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase (L-PGDS) and hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase (H-PGDS).


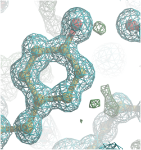

“The major reasons of high-quality crystal growth in space were thought to be the formation of a protein depletion zone (PDZ) and an impurity depletion zone (IDZ) around growing crystals due to the suppression of a convection flow. The transportation of a protein molecule and an impurity molecule toward the crystal is only dependent on the diffusive transport. As a result, the concentrations of the protein and the impurity around the crystal surface are decreased to slow down the crystal growth while reducing impurity uptake, resulting in highly ordered crystals with higher resolution and lower mosaicity. This also suppresses the nucleation on the crystal surface, which sometimes results in the suppression of cluster-like morphology to give a single crystal.”
Dr Hiroaki Tanaka, Confocal Science Inc.

Diamond Light Source is the UK's national synchrotron science facility, located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire.
Copyright © 2022 Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source Ltd
Diamond House
Harwell Science & Innovation Campus
Didcot
Oxfordshire
OX11 0DE
Diamond Light Source® and the Diamond logo are registered trademarks of Diamond Light Source Ltd
Registered in England and Wales at Diamond House, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot, Oxfordshire, OX11 0DE, United Kingdom. Company number: 4375679. VAT number: 287 461 957. Economic Operators Registration and Identification (EORI) number: GB287461957003.